Why Missiles?
Missiles are the great equalizers of modern warfare. They are the weapons that can turn the tide of a battle, destroy a city, or change the course of history. But the history of missiles is not just a story of destruction and devastation. It is a tale of innovation, creativity, and human ingenuity.
From their early development as primitive weapons of war to their current role as sophisticated tools of scientific exploration and military defense, missiles have transformed the world in countless ways. But why were missiles developed in the first place, and what has driven their continued evolution over the years?
At their core, missiles are all about power. Whether used for defense or aggression, missiles offer a means of exerting control over others from a distance. From the earliest days of human civilization, people have sought ways to harness this power to their advantage. The first missiles were likely simple projectiles made from sticks, stones, or other materials that could be thrown or launched at enemies. These early weapons were limited in range and accuracy, but they proved effective in close combat situations.
Early Development
 |
| Fig:- First Missiles were like this in ancient China |
The story of missiles begins in ancient China, where the first fire arrows were invented. These simple but effective missiles were designed to ignite upon impact, making them useful for attacking enemy fortifications. Over time, missile technology continued to evolve, with trebuchets, siege engines, and rockets being developed and used in warfare throughout the Middle Ages.
 |
| Fig:- The Paris Gun ,During WW1 |
But it was not until the 20th century that missile technology truly took off. The two World Wars marked significant milestones in missile development, with Germany introducing the first long-range rocket, the Paris Gun, during World War I. This weapon was capable of firing shells over 120 kilometers and was used to bombard Paris from a distance, causing significant damage to the city.
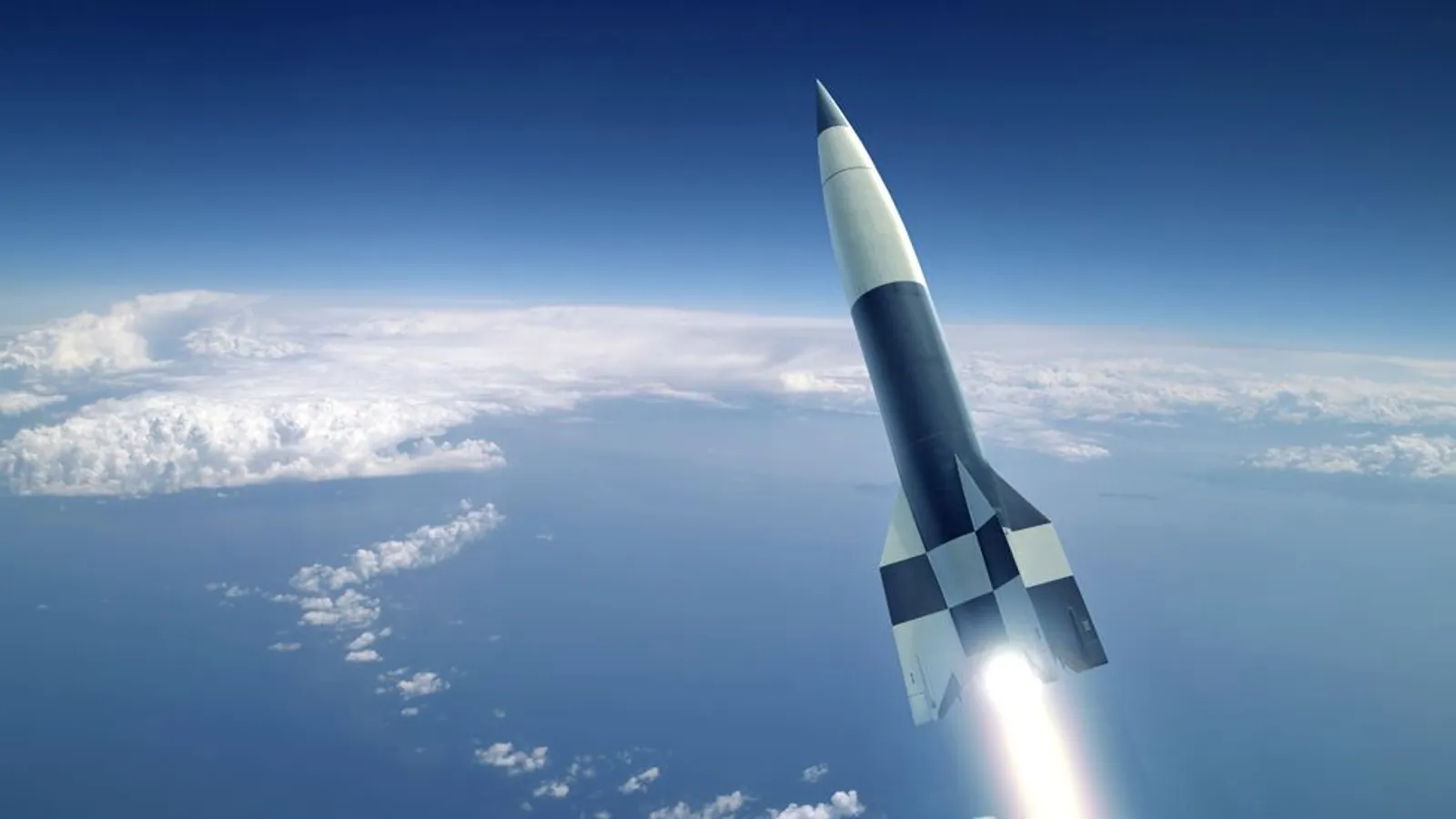 |
| Fig:- V-2 rocket developed by Germany (First to go in space) |
During World War II, both the Axis and Allied powers invested heavily in missile research and development. The Germans developed the V-1 and V-2 rockets, which were among the most advanced missiles of the time and were used to devastating effect against British and Allied targets. The V-2, in particular, was a significant technological achievement, and was the first missile to reach space.
Advancements in Missiles (the coming ages)
After the war, missile technology continued to advance, driven by both military and civilian applications. The Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union spurred a significant increase in missile research and development, as both sides sought to gain a technological advantage.
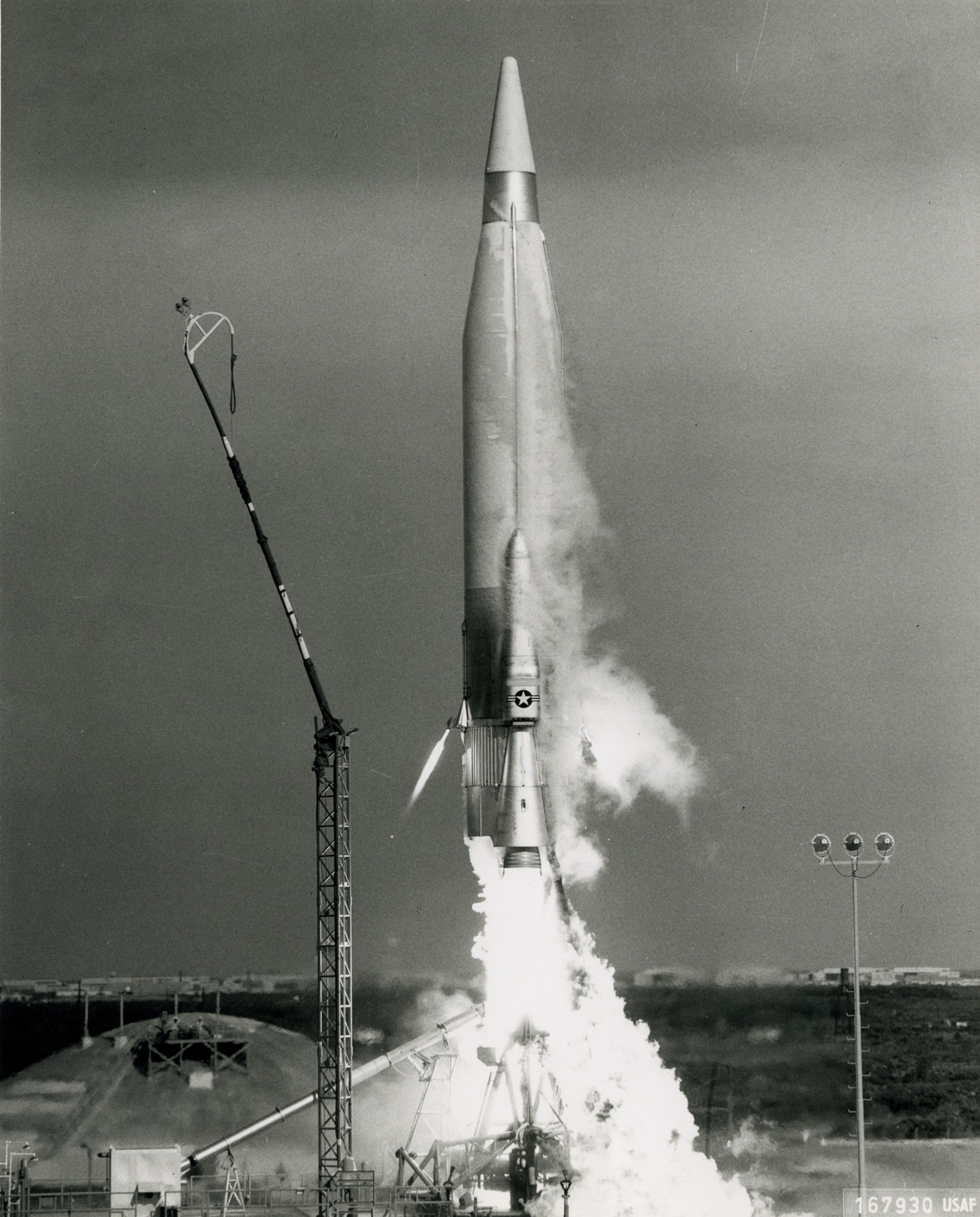 |
| Fig:- SM-65 Atlas ICBM |
During this time, missiles became more sophisticated and capable of carrying nuclear warheads. The development of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) marked a significant step forward in missile technology, allowing missiles to be launched from one continent to another with great accuracy. The first ICBM was developed by the Soviet Union in the late 1950s, and was capable of reaching targets up to 11,000 kilometers away.
As missile technology continued to advance, missiles became an increasingly important part of modern warfare. Today, missiles come in a variety of types and are used for a range of purposes, from air-to-air missiles that are designed to shoot down enemy aircraft, to surface-to-air missiles that can be used to defend against incoming attacks.
 |
| Fig:- Brahmos Supersonic Cruise Missile developed by Joint partnership of Russia and India |
One of the most well-known types of missile is the cruise missile, which is a self-guided missile that can be launched from a variety of platforms, including ships, submarines, and aircraft. Cruise missiles are highly accurate and can be used to strike targets with precision over long distances.
Future challenges
The development of missiles has not been without challenges. The accuracy and reliability of early missiles were often poor, and many missiles failed to hit their intended targets. In addition, missile technology was often prohibitively expensive, requiring significant investments in research and development.
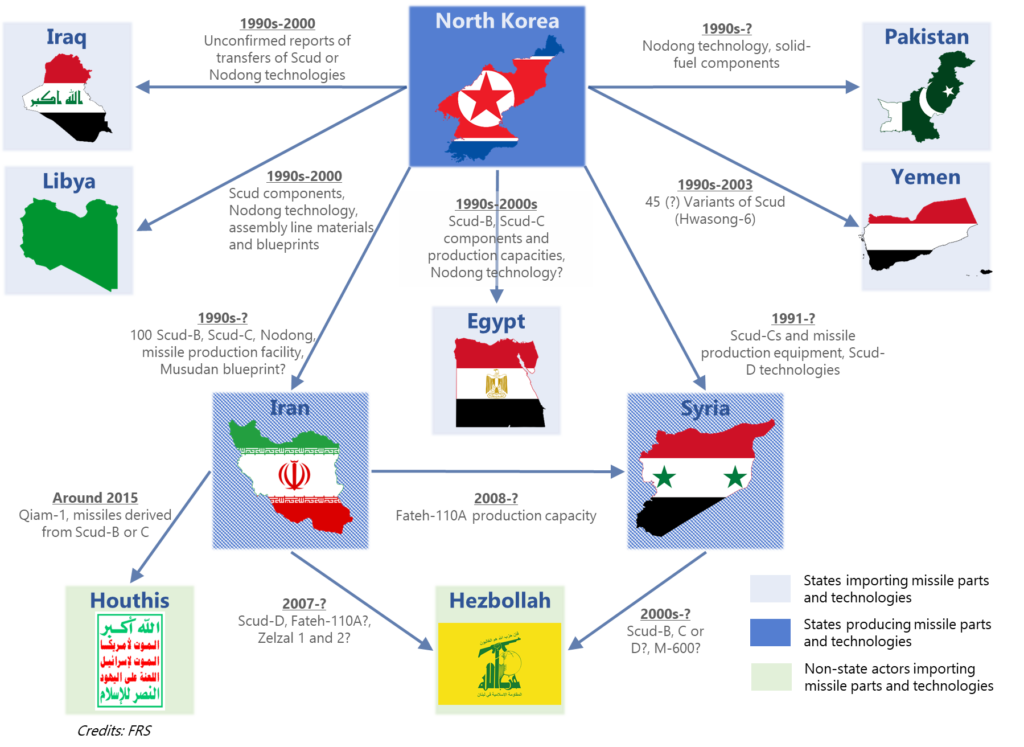 |
| Fig:- Ballistic Missile Proliferation in last decades |
A new challenge has arisen in recent years is the proliferation of missile technology to countries around the world. As more countries develop missile technology, the risk of missile attacks and the potential for conflict has increased.
Missiles in different sectors
 |
| Fig:-Hypersonic Missile Revolution : a new struggle for outer space |
Missiles are not just limited to warfare. They also have important civilian applications. For example, the space industry relies heavily on missile technology to launch satellites and conduct space exploration. Missiles are also used in scientific research, with rocketry playing a critical role in fields such as meteorology and astronomy.
Future of missiles
The future of missile technology is both exciting and uncertain. Advances in artificial intelligence, robotics, and materials science are likely to lead to significant breakthroughs in missile technology in the coming decades. However, the potential for missile technology to be used for malicious purposes, such as terrorism or war, is a constant concern.
 |
| Fig:- Hypersonic Missile |
To mitigate this risk, countries around the world have established a variety of treaties and agreements aimed at controlling the development and proliferation of missiles. One of the most well-known of these agreements is the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), which was established in 1987 to limit the spread of missile technology capable of carrying nuclear weapons.
 |
| Fig:- Hypersonic Attack Cruise Missile |
Despite these efforts, the reality is that missiles will likely continue to play a significant role in modern warfare and international relations for the foreseeable future. It is up to governments, military leaders, and researchers to ensure that this powerful technology is used responsibly and for the benefit of all humanity.
Conclusion
To summarize, the history of missiles is filled with human ingenuity and creativity, important milestones and groundbreaking achievements in technology. From ancient China’s fire arrows to today’s hyper-sonic missiles, development of missile technology changed the way the wars were fought and changed the world as we know it. Although, there are serious challenges that come with the missile technology, it also led to many important scientific achievements in exploration and communication. As we move forward in time, and the chances of large scale conflict are on the rise, it is hard to imagine a world without missiles or to predict what shape they will take in the future.